Osteitis Pubis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
Osteitis pubis is a painful condition that affects the pelvic area, specifically the pubic symphysis, where the left and right pubic bones meet. It is commonly experienced by athletes, as repetitive activities like running and kicking can irritate this joint. People with osteitis pubis often feel a sharp, localized pain in their lower abdomen or groin, which can be aggravated by physical activity. Other symptoms might include swelling or tenderness in the affected area. Understanding the causes and treatment options is essential for managing the discomfort and preventing further injury. Proper diagnosis often involves a physical examination and imaging tests. Rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medications are typically recommended, while physical therapy can help in recovery, ensuring a return to pain-free activities.
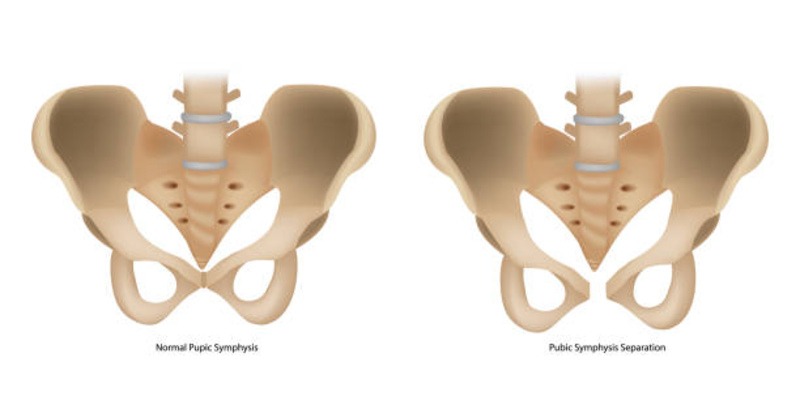
What is Osteitis Pubis?
Osteitis pubis, also known as pubic symphysis dysfunction or athletic pubalgia, is a condition that involves inflammation of the pubic symphysis joint. This joint connects the two pelvic bones at the front of the pelvis and helps support the body's weight during movement. Osteitis pubis can range from mild discomfort to severe pain and can significantly impact an individual's daily activities, especially those that involve repetitive movements or strain on the pelvic area.
Symptoms of Osteitis Pubis
The most common symptom of osteitis pubis is pain in the lower abdomen or groin area. This pain can be sharp and localized or diffuse and may radiate to the hips, thighs, or buttocks. The discomfort may worsen with physical activity like running, jumping, or twisting movements. Other symptoms that an individual with osteitis pubis may experience include:
- Swelling and tenderness at the front of the pelvis
- Stiffness in the pelvic region
- Difficulty walking, standing, or sitting for extended periods
- Pain during sexual intercourse
It's crucial to seek medical attention if these symptoms persist or interfere with daily activities.
What Causes Osteitis Pubis?
Osteitis pubis is commonly seen in athletes or individuals who participate in activities that involve repetitive strain on the pelvic area. Some common causes of osteitis pubis include:
- Overuse or repetitive movements like running, jumping, or kicking
- Muscle imbalances in the pelvic region
- Poor posture or body mechanics
- Previous injuries to the pelvis or groin area
It's also important to note that certain risk factors may increase an individual's likelihood of developing osteitis pubis. These include conditions like arthritis and osteoporosis.
Diagnosis of Osteitis Pubis
If an individual experiences symptoms consistent with osteitis pubis, they should see a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. A physical examination of the pelvic area will be conducted, including assessing range of motion and identifying tender areas. Imaging tests like X-rays, MRI scans, or bone scans may also be used to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options for Osteitis Pubis
The primary goal of treating osteitis pubis is to reduce pain and inflammation while promoting healing in the affected area. Some common treatment options include:
Rest and Ice
One of the first steps in managing osteitis pubis is to allow for adequate rest. This involves avoiding activities that worsen the pain, such as sports or exercises that involve running, jumping, or significant stretching of the pelvic area. Ice can be applied several times a day to help reduce swelling and provide relief from pain. Typically, ice should be wrapped in a cloth and applied to the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time.
Anti-inflammatory Medications
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can be recommended to help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. These medications are usually prescribed for short-term use during flare-ups, and individuals should follow their healthcare provider's guidance regarding dosage and duration.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the treatment and rehabilitation of osteitis pubis. A physical therapist will develop a personalized exercise program focused on strengthening the muscles around the pelvis and improving flexibility. This may include exercises that target the core, hips, and lower back to ensure proper support and alignment of the pelvic region. Stretching exercises may also be included to alleviate muscle tension and improve range of motion.
Alternative Treatments
In some cases, other interventions such as corticosteroid injections may be recommended to reduce severe inflammation and pain. Additionally, individuals may explore alternative therapies like acupuncture or chiropractic care, which some patients find beneficial in managing symptoms and improving overall well-being.
When surgery is considered necessary?
Surgery is typically considered a last resort in treating osteitis pubis. It may be recommended if conservative treatment options do not provide significant relief, and symptoms persist for an extended period. Surgical interventions for osteitis pubis involve removing any damaged tissue or repairing the pubic symphysis joint.
Prevention of Osteitis Pubis

While there is no foolproof way to prevent osteitis pubis, there are steps that individuals can take to reduce their risk of developing this condition. These include:
- Maintaining Proper Technique: Engaging in correct posture and form when participating in physical activities can minimize unnecessary strain on the pelvis. Undergoing professional training or consultation can help ensure that techniques are performed correctly.
- Regular Exercise and Stretching: Incorporating exercises that enhance core strength and flexibility can provide better support to the pelvic region. Stretching routines should focus on the hips, thighs, and lower back to maintain balanced muscle development and reduce tension.
- Gradual Progression: When beginning a new exercise program or increasing activity levels, it's important to progress gradually to allow the body time to adapt. Sudden increases in intensity or duration can lead to overuse injuries such as osteitis pubis.
- Wearing Appropriate Gear: Using supportive footwear and proper athletic equipment can reduce the risk of injury by ensuring better stability and alignment during physical activities. For athletes, equipment like custom orthotics may aid in maintaining pelvic alignment.
Taking these preventive measures can significantly lower the chances of developing osteitis pubis and enable a healthy, active lifestyle.
Conclusion
Osteitis pubis is a challenging condition that can significantly impact an individual's ability to engage in physical activities and perform daily tasks. However, with early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and preventive measures, individuals can manage symptoms effectively and reduce the risk of recurrence. Rest and rehabilitation are crucial for recovery, and incorporating preventative strategies into one's routine can promote long-term pelvic health. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, patients are better equipped to make informed decisions alongside their healthcare providers, ensuring the best outcomes for their specific needs.